OCCUPANCY PLANNING
FUNDAMENTALS
METRICS
GPS has established key terms and definitions to ensure consistency in measurement methods. This page shows the critical metrics used to measure our spaces and understand supply and demand performance. At this point, not all information listed is tracked in all locations. As our planning process become more standardized globally, the data availability will improve and allow for further automation.
Key Terms
A full list of Occupancy Planning terms is in the GPS Standards Glossary.
Data Metrics
Capacity
How many people the building holds
Building Headcount, Occupancy Rate
How many people are assigned to the building
Traffic Count, Presence Rate, Activity Rate
Ways to measure how many people are using the building
Square Foot + Square Meter Measurements
There are different categories of how a building is measured, each with a different use case. For accuracy, it's important to be clear which is being used.
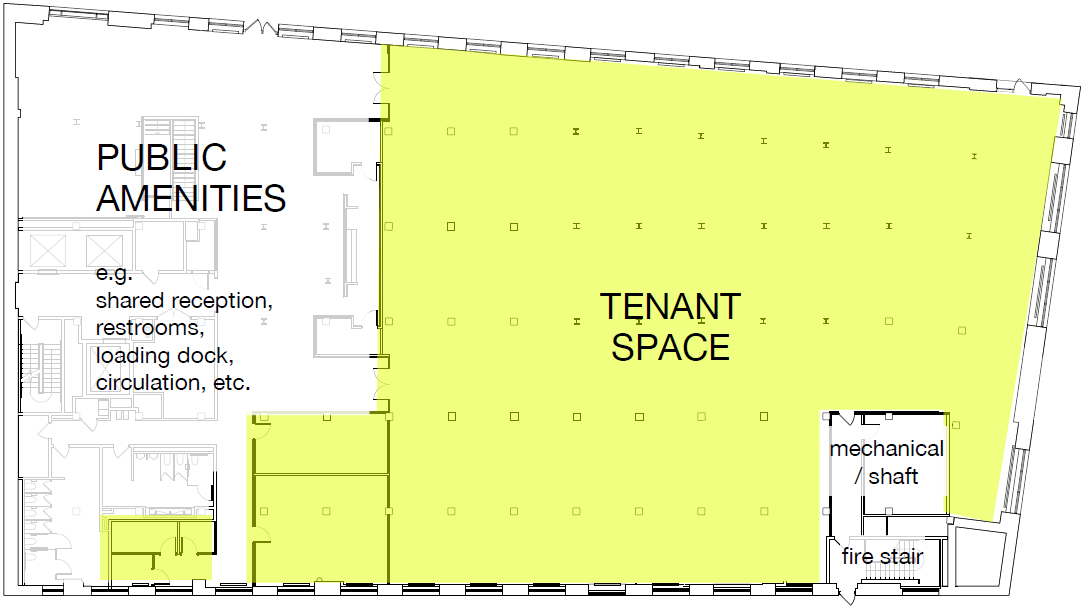
Usable Square Feet (USF) or Net Square Meters (NIA)
Use case: Occupancy planning and architectural programming. This can be applied to a leased site or an owned building.
There are regional nuances for how this is measured. Generally includes private tenant hallways, private restrooms, and columns, but excludes unusable areas (e.g., mechanical rooms, shafts, vertical circulation) or public restrooms, public circulation, and other shared areas.
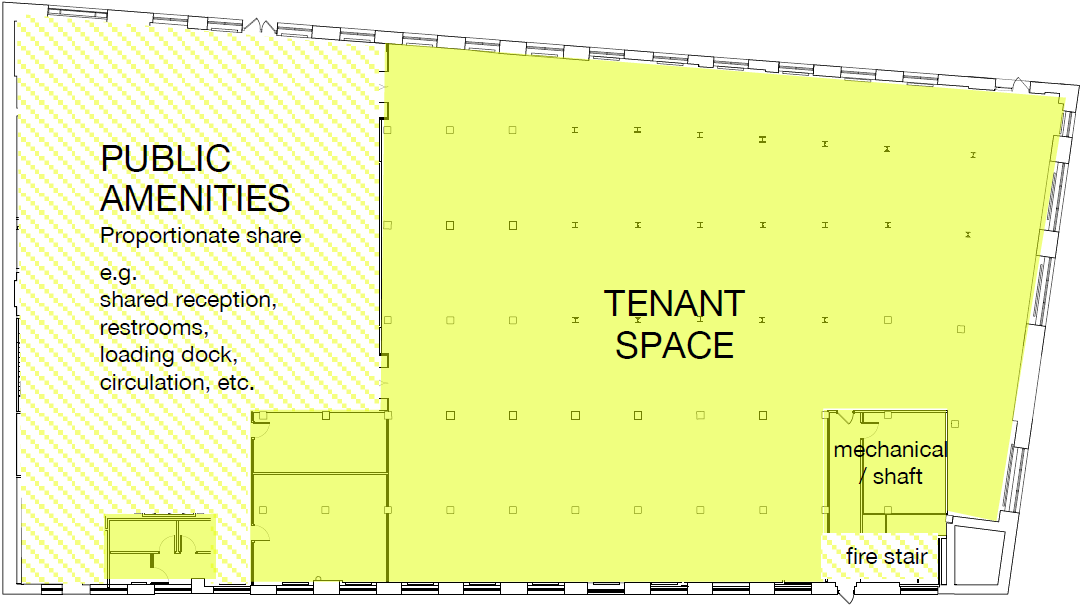
Rentable SF / SM
Use case: Lease information and evaluation.
Includes the tenant's usable area and their proportionate share of common building areas such as lobbies, circulation, restrooms, and mechanical rooms. The number is determined by the landlord; measurement methods vary. Always use the number documented from the lease vs. measuring the floorplan.
Gross SF / SM
Use case: Used least often. Typically only referred to for owned buildings or when a tenant has an entire building.
Includes everything, even unusable space between walls and vertical circulation.