UNIVERSAL DESIGN
FUNDAMENTALS
OVERVIEW
An equal playing field begins in our workplace. It begins with us.
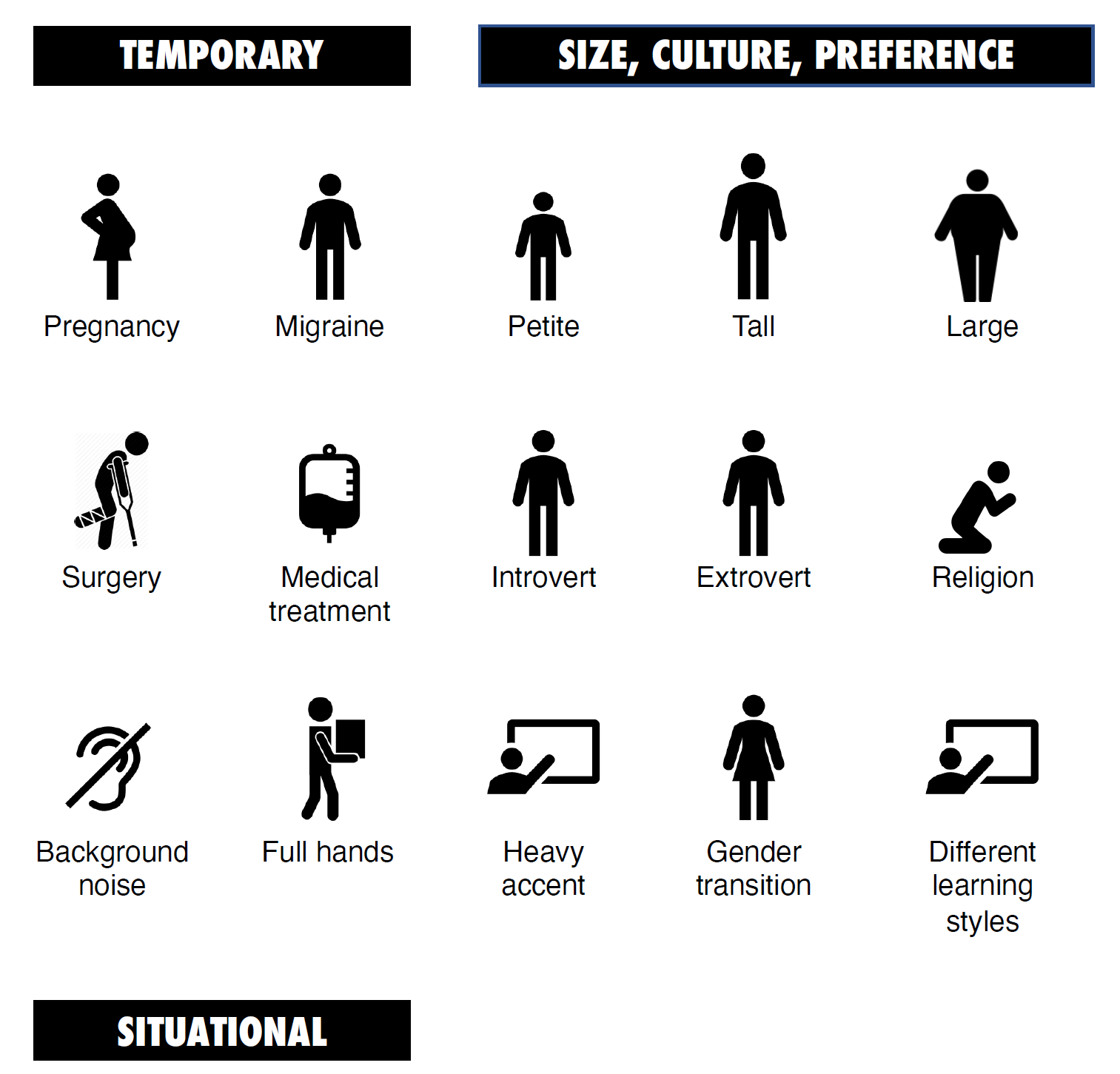
Universal Design is a foundational way of thinking. It’s not a checklist or set of requirements. It’s the concept of designing for a broad range of users, so everyone can participate. It’s a way to ensure that our workplace is inclusive and accessible to welcome greater diversity to the Nike family.
Our Definition of "Broad Range"
Universal Design often does not cost more. By designing for a broad range of people from the beginning, we can reduce the need for individual accommodations later. The concept was originally created by architects, but it is now used for product design, digital technology, education, and service design.
Examples
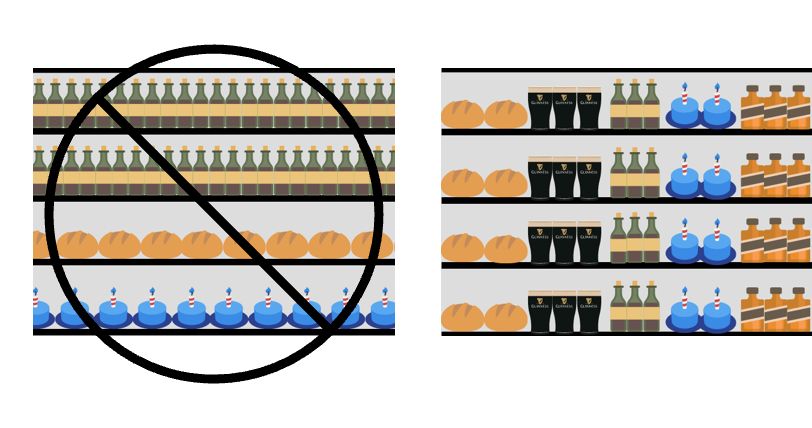
Universal Design is Good Design
Universal design is essential for 15% of the population who have disabilities (according to the World Health Organization). Excluding them from the design means excluding them from the environment.
For around 40% of the population, Universal design will enhance the quality of their experience, allowing them greater participation and more equitable experience. And universal design is good for 100% of people.